Investors are always on the lookout for ways to make the most of their investments.
If you are one of them, then it's crucial to understand the preferred dividend coverage ratio, which can help you assess a company's financial health and its ability to pay dividends.
The preferred dividend coverage ratio is a critical financial ratio that measures a company's ability to cover its preferred dividends with its net income.
It's calculated by dividing the company's annual net income by its preferred dividend payment for that year.
A ratio above 1 indicates that the company can meet its preferred dividend payment with its net income, while a ratio below 1 suggests that the company may struggle to pay dividends.
The preferred dividend coverage ratio can be a useful tool for investors to identify financially stable companies with a solid track record of paying dividends.
This, in turn, provides peace of mind to investors, as they know they are investing in a company that is likely to continue paying dividends in the future.
Understanding the preferred dividend coverage ratio can also help investors make informed investment decisions.
For example, if a company has a low preferred dividend coverage ratio, it may be an indicator that the company is not financially stable and may not be able to pay dividends in the future.
On the other hand, a company with a high preferred dividend coverage ratio is a sign that it's worth considering for your portfolio.
To calculate the preferred dividend coverage ratio, you need to know the annual net income and the annual preferred dividend payment for that year, which can be found in a company's financial statements.
With this information, you can use the preferred dividend coverage ratio calculator to find the ratio.
Understanding the preferred dividend coverage ratio is essential for investors who want to maximize their investments.
It can help you identify financially stable companies and make informed investment decisions.
By using the dividend coverage ratio formula, you can calculate the ratio and determine whether a company is worth investing in or not.
So, dive into this comprehensive guide and unlock the power of the preferred dividend coverage ratio.
Definition - What is Preferred Dividend Coverage Ratio?
The company’s preferred dividend coverage ratio, also known as dividend cover, is a valuation ratio that determines whether a company has made enough profit to meet its preferred dividend obligation.
This ratio is calculated by dividing the company's net income by the total required preferred dividend payments.
The result is a figure that gives shareholders an idea of the relative burden the outstanding preferred shares would have on the company.
The preferred dividend coverage ratio is especially important for shareholders as it helps them understand whether a company can pay a fixed dividend to common shareholders while also meeting its preferred dividend obligation.
This ratio is often included in a preferred issue’s prospectus, which outlines the terms of the preferred stock being offered.
A high ratio would indicate that a company is generating enough income to cover its preferred dividend payments, which is positive news for investors.
In contrast, a low ratio would suggest that the company is struggling to generate enough income to meet its preferred dividend obligations.
In such a scenario, the company may be forced to cut its dividend payments, which can negatively impact investors.
The preferred dividend coverage ratio is a vital metric that provides insight into a company’s ability to meet its financial obligations to its preferred shareholders while still providing dividends to its common shareholders.
It's important to note that the preferred dividend coverage ratio is just one of the many financial metrics that investors should consider before making any investment decisions.
It should be used in conjunction with other ratios, such as debt-to-equity, price-to-earnings, and return on common equity, to get a comprehensive understanding of the company's financial position.
Furthermore, it's worth mentioning that the preferred dividend coverage ratio can vary across industries and companies.
For example, a utility company that has a stable revenue stream and predictable cash flows may have a higher preferred dividend coverage ratio compared to a startup in a high-risk industry that is not generating profits yet.
The preferred dividend coverage ratio is a valuable tool that helps investors and analysts assess a company's ability to meet its financial obligations to its preferred shareholders.
It is an essential metric to consider when evaluating the attractiveness of preferred stocks and provides valuable insights into a company's financial health.
Formula
The simple formula for finding the preferred dividend coverage ratio involves dividing the total net income by the required amount of preferred dividend payout.

Preferred Dividend Coverage Ratio = Net Income / Preferred Dividend
An important thing to remember is that the required preferred dividend amount includes any accrued amount from previously unpaid dividends.
Example
Company B has reported a net income of $500,000 for the quarter. The company is required to pay out 7% on all preferred shares.
There are 55,000 preferred shares valued at $16.50 per share. They have so far been paying out preferred dividends steadily and have no outstanding balance.
Using the formula, the equation would be:
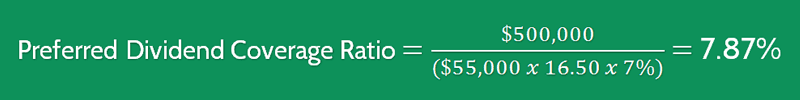
This is a strong sign that the company will not only be able to pay out its preferred dividends but also pay dividends to its common shareholders as well.
In general, what you are looking for is a number as far above 1 as possible.
Interpretation & Analysis
A crucial factor to consider when assessing a company's financial health is whether the company can cover its annual dividend dollar amount.
This is where the concept of dividend coverage ratio comes into play.
The dividend coverage ratio measures how many times a company's current level of dividend can be paid out of its equal cash flow.
It is essential to note that a high dividend coverage ratio means that a company has sufficient funds to cover not only the dividend amount for that year but also any unexpected expenses or future investments.
When it comes to paying the highest preferred dividend, it's not enough to show that a company is just barely capable of paying out those dividends.
Ideally, what one wants to see is a high enough preferred dividend coverage ratio that the company has no trouble paying dividends to preferred shareholders.
However, it's equally crucial for common shareholders to note that a high ratio such as the one in the example above is even more important.
This gives them an idea of how likely they are to see any dividends themselves.
To calculate the dividend coverage ratio, divide the total amount of dividends paid by the company by its net income.
For instance, if a company has paid $100,000 in dividends and has a net income of $200,000, its dividend coverage ratio would be 0.5.
In the example given earlier, the company was able to pay out preferred dividends and still had plenty leftover, which means they would be in a stronger position to offer dividends to its common shareholders as well.
Ultimately, having a high dividend coverage ratio is an essential factor in determining a company's financial health and long-term sustainability.
Cautions & Further Explanation
Understanding a company’s ability to meet its financial obligations can be done by analyzing various coverage ratios.
One of these ratios is the dividend coverage ratio (DCR), which is a guide to dividend-paying companies' financial health.
DCR is calculated by dividing the company's net income by the total amount of preferred dividends it needs to pay annually.
A DCR above 2 indicates that a company has twice the amount available to make dividend payments, making it financially stable.
When analyzing a company's DCR, it is important to consider whether it pays dividends at all and instead compare it to another company that also does not pay dividends.
This is because dividends are not a requirement or a standard across the market.
Therefore, comparing a company with a low preferred dividend coverage ratio to a non-dividend paying company is not very accurate.
It is also essential to note that preferred dividends are cumulative, which means that if a company is unable to pay them in a given quarter, the amount owed will rollover into the next dividend payout.
This feature means that as a preferred shareholder, you do not need to worry too much if the company misses a payout.
Natural fluctuations in cash flow and expenses over the year can influence a company's decision to payout dividends in a given quarter.
Therefore, missing one dividend payment should not immediately be taken as a cause for concern.
It is only when a company consistently fails to meet its obligation to make dividend payments that you should start worrying.
In such a case, it might be necessary to use a dividend coverage ratio calculator to determine the number of times a company can pay dividends based on its current financial position.
Overall, analyzing a company's DCR is an important step in understanding its financial health and making informed investment decisions.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: What is a preferred dividend coverage ratio?
A preferred dividend coverage ratio is a financial metric used to measure a company's ability to pay dividends to its preferred stockholders. It compares the company's earnings to the amount of dividends it pays to its preferred stockholders.
Q: How is the preferred dividend coverage ratio calculated?
The preferred dividend coverage ratio is calculated by dividing the company's earnings available for paying preferred dividends by the amount of preferred dividends paid during a specific period. The result is expressed as a ratio, which indicates how many times the company's earnings cover its preferred dividends.
Q: Why is the preferred dividend coverage ratio important?
The preferred dividend coverage ratio is important because it provides insight into a company's financial health and its ability to meet its obligations to its preferred stockholders. If a company has a low preferred dividend coverage ratio, it may be at risk of not being able to pay its preferred dividends.
Q: What is a good preferred dividend coverage ratio?
A good preferred dividend coverage ratio varies by industry and depends on several factors, such as the company's growth prospects, financial stability, and debt levels. Generally, a ratio of 2 or higher is considered good, as it indicates that the company's earnings can cover its preferred dividends twice over. However, investors should consider other factors as well before making investment decisions.
Final Words
Success can be defined in many ways, from having more time for family and friends to owning a bigger house or going on vacations.
But one thing we all agree on is that achieving success requires the right financial ratio analysis method.
An important aspect of financial planning is understanding your preferred dividend coverage ratio.
This metric is an indicator of future risk and tells you how much of your preferred dividends are covered by your company's earnings.
A high preferred dividend coverage ratio is essential because it ensures that a company can pay its dividends to its shareholders.
If a company has issues with the ratio, there is a risk of not receiving dividends in the future.
Therefore, it's essential to look at the preferred dividend coverage ratio when investing in a company.
So, what is a good preferred dividend coverage ratio?
While it can vary by industry, a ratio of 2 or higher is generally considered good.
This means that a company's earnings are at least twice as much as its preferred dividends.
For example, if a company reports annual earnings of $10 million and pays dividends of $5 million, its preferred dividend coverage ratio would be 2.
However, it's crucial to note that having a high preferred dividend coverage ratio doesn't necessarily mean a company can pay dividends to its shareholders.
There have been instances where companies have a high ratio of, say, 40 times, but yet have no cash to pay dividends.
Therefore, it's crucial to assess a company's level of dividends and whether they're sustainable.
Prioritizing your preferred dividend coverage ratio can set you up for long-term financial stability and success.
It's not just about the number; it's also about the actions you take to get there.
Investing in companies with a strong financial track record is essential.
Also, keeping an eye on your preferred dividends can ensure that they're sustainable.
In conclusion, achieving success requires the right financial planning.
A crucial aspect of financial planning is understanding your preferred dividend coverage ratio.
This ratio is an essential indicator of a company's ability to pay its dividends to its shareholders.
By investing in companies with a high preferred dividend coverage ratio, you can reduce the risk of not receiving dividends in the future.


