Are you an investor who wants to maximize your investment portfolio?
Have you invested in stocks that don't seem to pay off?
If you answered yes to either of these questions, then you need to learn about the dividend coverage ratio - a financial metric that can make a significant difference in your investment success!
The dividend coverage ratio, also known as the dividend cover, is a measure of a company's ability to pay dividends to its shareholders.
This ratio is calculated by dividing the company's earnings by the dividends paid to shareholders.
A high dividend coverage ratio indicates that a company can easily cover its dividend payments, which is good news for investors.
This ratio is important for investors because a company with a high dividend coverage ratio is more likely to pay consistent dividends.
This is excellent news for investors who rely on regular income from their investments.
Furthermore, a high dividend coverage ratio can also indicate that a company is financially stable and well-managed, making it a safer investment option.
However, not all companies have high dividend coverage ratios, and not all high ratios are created equal.
It's essential to understand how to interpret this ratio and use it to make informed investment decisions.
The dividend coverage ratio formula is used to determine the level of dividend payout a company can maintain based on its earnings.
It can also help identify any issues with the ratio, such as when a company may be overextending itself and not able to cover the required preferred dividend payments.
In this guide to dividend coverage ratios, we will explore everything you need to know about this metric, including how to calculate it, how to use it to evaluate a company's financial health, and how to incorporate it into your investment strategy.
By learning about dividend coverage ratios, you can make informed investment decisions that can help maximize your investment portfolio.
So, what are you waiting for?
Dive into our guide and unlock the secrets to successful investing with the dividend coverage ratio!
Definition - What is Dividend Coverage Ratio?
The dividend coverage ratio, also known as the dividend cover ratio, is a business valuation ratio used to measure a company's ability to pay dividends to its shareholders.
This ratio is calculated by dividing the company's net income by the dividend payout to shareholders.
Essentially, this ratio measures the number of times a company can pay dividends to its shareholders using the profits it has earned during a specific period.
The dividend cover ratio is commonly used by investors to determine the number of times a company can pay dividends to its shareholders.
Typically, a higher ratio suggests that a company is capable of paying dividends several times over, which makes it a less risky investment.
On the other hand, a lower ratio indicates that a company may be unable to sustain its current dividend payout, or worse, it might have to borrow money in order to pay dividends, which is not a sustainable practice and a cause for concern for investors.
The dividend payout ratio is another metric that shows the percentage of earnings of a company that is paid out as dividends to shareholders.
It indicates that a company is committed to sharing its profits with its shareholders, which can be seen as a positive signal for investors.
However, a high dividend payout ratio may also suggest that the company is not investing enough in its growth and expansion, which could limit its future profitability.
The dividend coverage ratio and the dividend payout ratio are important metrics that investors use to evaluate a company's financial health and its potential as an investment.
A high dividend coverage ratio and a moderate dividend payout ratio generally indicate that a company is financially stable, profitable, and committed to sharing its profits with shareholders.
Conversely, a low dividend coverage ratio and a high dividend payout ratio could suggest that a company may not be a wise investment due to the risks associated with unsustainable dividend payouts.
Formula
The simple formula to measure the dividend coverage is as follows:

Dividend Coverage Ratio = Annual Net Income / Annual Dividends Paid To Common Shareholders
However, this would then take into account preferred dividend payments which are not available to common shareholders. Instead, we would use the following:

Dividend Coverage Ratio = (Net Income - Dividend Paid On Irredeemable Preference Shares) / Dividend Paid To Ordinary Shareholders
So divide profit after tax less dividends paid on irredeemable preference shares as these payments are not available to common shareholders by dividends paid to ordinary shareholders.
You can find these numbers on a company’s income statement.
Example
Okay now let’s consider a quick example so you can see how easy it is to calculate this ratio.
YBO Company has reported annual earnings of $1,500,000. It must pay $250,000 per year to its preferred shareholders and paid out $470,000 in dividends to its ordinary shareholders in the past year.
To determine the dividend cover ratio, we need to substitute into the formula:
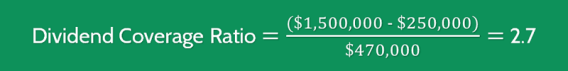
This suggests that YBO Company can pay dividends to its shareholders 2.7 times from the profits it has earned during the period.
Interpretation & Analysis
A dividend cover ratio is an essential financial metric that indicates how much cash a company has available to make dividend payments to its shareholders.
This ratio is calculated by dividing the company's earnings per share (EPS) by the dividend per share (DPS) and is usually expressed as a ratio or a percentage.
Typically, a high dividend cover is seen as being a good measure, with a ratio above 2 indicating that a company can cover its current level of dividend payments and cushion for any uncertainties that may arise.
However, the higher the dividend cover, the more cash the company is retaining, which could be used for other purposes such as investments, acquisitions, or expansion.
On the other hand, a lower dividend cover may be adequate depending on the stability within the organization.
The dividend cover ratio calculator can help investors evaluate a company's ability to pay dividends.
A dividend coverage ratio that consistently falls below 1.5 would be a cause for concern, as it would suggest that the business may not be able to maintain the level of dividends if anything has an adverse effect on its profitability in the future.
The dividend coverage ratio is an important factor for preferred stock investors because they need to ensure that the company can cover the preferred dividend amount before paying any dividends to common shareholders.
The dividend coverage ratio is an essential metric that investors should monitor to ensure that a company's payout is enough to cover its current dividend and maintain its financial stability.
Cautions & Further Explanation
The dividend cover ratio is an important metric used by investors to determine the sustainability of a company's dividends to common shareholders.
It is calculated by dividing a company's net income by the annual dividend paid out to shareholders.
A DCR above 2 is generally considered a good sign, indicating that a company's ability to pay its dividends is strong.
However, using net income as a basis for the calculation can be problematic.
While high net income may imply that a company is generating enough cash to make dividend payments, this is not always the case.
There are times that a company may report high earnings but have little cash available to make dividend payments.
Additionally, net income does not necessarily act as an indicator of future risk.
A company's net income can change dramatically due to unforeseen events, and a DCR of 1.5 may be a cause for concern.
Investors should also be aware that the number of times a company can pay its dividend is not always a reliable measure of the sustainability of a company's dividends.
While a higher dividend coverage may indicate a company's ability to pay dividends, it does not necessarily guarantee the sustainability of the dividend in the future.
Therefore, it is important for investors to look beyond just the DCR and consider other factors such as the company's financial health and future prospects when assessing the sustainability of its dividends.
Investors should consider using this valuation ratio in conjunction with other financial ratios to paint a full picture of a company's financial position.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: What is dividend coverage ratio?
Dividend coverage ratio is a financial metric that indicates a company's ability to pay its dividends from its earnings. It is calculated by dividing the company's net income by the dividends paid to shareholders.
Q: How is dividend cover ratio useful?
Dividend coverage ratio can help investors assess the sustainability of a company's dividend payments. If the ratio is high, it suggests that the company has sufficient earnings to cover its dividend payments. If the ratio is low, it could indicate that the company may struggle to maintain its current dividend payments.
Q: What is a good dividend coverage ratio?
A good dividend coverage ratio typically depends on the industry and the company's individual circumstances. As a general rule, a ratio of 1.5 or higher is considered healthy, indicating that the company can comfortably cover its dividend payments with its earnings. However, investors should also consider other factors, such as the company's growth prospects and financial health.
Q: How can dividend coverage ratio be improved?
To improve dividend coverage ratio, a company can focus on increasing its earnings, reducing its dividend payments, or a combination of both. This may involve strategies such as increasing sales, improving profit margins, reducing expenses, or cutting back on dividend payments. However, it is important to balance the need to maintain a sustainable dividend with the need to invest in the company's growth and future success.
Wrap Up: DCR Made Simple!
Congratulations, you've made it to the end of this article!
I hope you've gained valuable insights on how to manage your investments and maximize your returns.
Now, let's bring our discussion of dividend coverage ratio to a close.
Imagine waking up every morning, feeling secure and confident about your finances.
You've got your investment portfolio in order, and your dividend income is providing a steady stream of cash flow.
What a great feeling that would be, right?
Well, that's where the dividend coverage ratio (DCR) comes in.
This financial metric can help you assess a company's ability to make dividend payments to its shareholders.
It is used to determine the number of times a company may sustain its current level of dividend payments based on its earnings.
The DCR is a useful tool to evaluate a company's financial health.
If a company has a high DCR, it means that it is generating enough earnings to cover its dividend payments.
A DCR of 2, for example, indicates that a company's earnings are twice its dividend payments.
On the other hand, a low DCR may suggest that the company is struggling to sustain its current level of dividend payments.
This could mean that the company may not be able to pay dividends to preferred shareholders, or worse, may not be able to pay dividends at all and instead may need to reinvest into the business.
To calculate the DCR, divide the company's earnings per share (EPS) by its dividend per share (DPS).
If the ratio is greater than one, the company is generating enough earnings to cover its dividend payments.
The DCR can also be used to determine if a company has enough earnings to pay dividends to its common shareholders after paying dividends to preferred shareholders.
So, what are you waiting for?
Start analyzing companies' dividend coverage ratios and build a diversified portfolio of stocks that will pay you a steady stream of dividends.
Remember, practice makes perfect.
Keep learning and applying your knowledge to become a successful investor.
Thank you for reading, and good luck with your investments!


