Are you an investor looking to maximize your returns and earn more from your investments without taking on additional risks?
If yes, then you've come to the right place.
One of the essential metrics for investors to consider is the return on common stockholders equity.
This key performance indicator measures how effectively a company is using shareholder equity to generate profits.
It's a way to determine if a company is making enough money to justify the investment you've made in their stock.
If the return on common stockholders equity is high, that means you're likely to see a higher return on your investment.
To understand how to maximize your return on common stockholders equity, you need to analyze this key metric and identify the factors that influence it.
You can start by examining the balance sheet and income statement of a company to calculate its ROE ratio, which is equal to a company’s net income divided by its average shareholders’ equity.
Public traded companies also disclose this information in their financial statements.
Moreover, debt is another factor that affects the return on common stockholders equity.
While a company may use debt to finance its operations, excess debt can lead to financial strain and lower returns.
Therefore, it's crucial to evaluate a company's debt levels and its ability to pay off its obligations.
The total equity of a company also plays a significant role in its return on common stockholders equity.
By increasing their total equity, companies can generate more income and, therefore, increase their ROE ratio.
To achieve this, companies can either retain their earnings or issue new shares to raise additional capital.
Industry trends and market conditions can also impact a company's ROE ratio.
For instance, companies operating in a booming industry may experience higher returns due to increased demand, while those in a declining industry may struggle to generate profits.
Maximizing your return on common stockholders equity requires careful analysis of a company's balance sheet, income statement, debt levels, and total equity.
It's also essential to consider industry trends and market conditions to make informed investment decisions that align with your financial goals.
By implementing practical strategies, you can improve your investment portfolio and boost your returns.
So, dive into the article and discover the secrets to maximizing your return on common stockholders equity today!
Definition - What is Return on Common Stockholders Equity (ROCE)?
The return on common stockholders equity ratio, also known as ROE, is a vital metric used for evaluating a company's financial health.
It measures the returns that a company can generate from the equity that its common shareholders have invested in it.
This equity ratio analysis is a useful tool for both investors who already own shares in a company and those who are considering it as an investment opportunity.
To calculate the ROE, the net income of a firm is divided by the common shareholders' equity.
The higher the ROE, the more proficient the company is at generating profits from equity.
The average return on equity for the industry and the company's past performance should be taken into account when calculating a company's ROE.
When examining a company's ROE, it's important to consider excessive debt as it can have an adverse effect on the ratio.
A high ROE can also indicate a reliance on debt to fund operations and growth, which can pose risks to the company's financial stability.
A company with a lower ROE but a solid balance sheet and steady growth potential may be a better investment than one with a higher ROE that has a high level of debt.
As an investor, the return on common equity shareholders is a crucial metric that not only shows how effectively a company is using shareholders' money to generate returns, but also highlights the efficiency of the firm's management in using equity to support operations and fund growth.
Therefore, when evaluating an investment opportunity, examining a company's ROE should be a part of the investment analysis process.
Formula
When you want to calculate the return on shareholders' equity for a particular company, you can use the following formula:
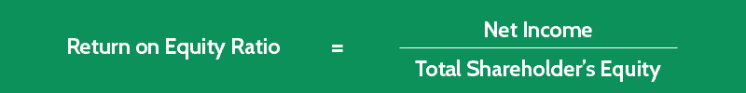
Return on Equity Ratio = Net Income / Total Shareholders' Equity
Since most investors are common shareholders, it’s not uncommon to see this formula adjusted to account for any profit that’s earmarked for the payment of preferred share dividends.
In this case, the amount of the preferred stock dividends for the relevant period would be subtracted from the firm’s net income (Net Income – Preferred Stock Dividends).
The shareholder equity amount used in the formula is usually averaged for the period being evaluated.
Return on Common Stockholders Equity Calculator
Example
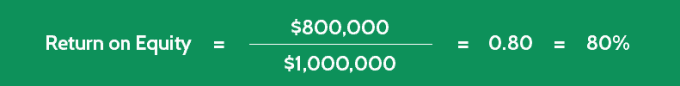
Perhaps you already own shares in Company FF, and you’d like to measure its return on common stockholders' equity for the past year.
When you examine Company FF’s financial statements, you find the following information:
- Net Income = $900,000
- Preferred Stock Dividends = $100,000
- Opening Common Shareholder Equity = $800,000
- Closing Common Shareholder Equity = $1,200,000
For calculating the return on common shareholders equity, we will:
- Adjust the Net Income by subtracting the preferred stock dividends
- Calculate the Average Common Equity by summing the opening and ending equity and then dividing the result by 2
- Plug the Adjusted Net Income and the Average Common Equity into the formula
Interpretation & Analysis
The return on common shareholders' equity ratio is a financial metric that is used to measure a company's ability to generate profits for equity investors.
This ratio is expressed in percentage and can be calculated by dividing net income by the total common shareholder equity.
A higher return on common equity ratio indicates that a company is generating higher profits from the net assets that have been invested by shareholders.
However, it is important to note that the acceptable level of return on equity may vary from industry to industry.
Therefore, it is crucial to compare a company's return on equity to that of other companies within the same industry.
This will help to determine whether the company is performing well or not.
Apart from measuring a company's current profitability, the return on common stockholders' equity ratio can also be used to evaluate the historical financial performance of a business over a period of time.
This ratio considers both the income statement and the balance sheet to determine how well a company is utilizing retained earnings to generate profits.
In summary, return on common shareholders' equity ratio is a useful metric that can be used to measure a company's profitability and historical financial performance.
It is important to compare a company's return on equity to that of other companies within the same industry to determine whether it is performing well or not.
A higher return on equity indicates that a company is generating higher profits for equity investors from the net assets invested.
Cautions & Further Explanation
Return on Equity (ROE) is an important financial metric that can be used to gauge a company's profitability and efficiency in generating profits from the common shareholders' investments.
There are several strategies that a company can employ to improve its ROE.
One approach is to decrease the total amount of shareholder equity, which can be achieved by buying back some of its own shares from investors.
However, this strategy can have potential drawbacks for the company's financial health, particularly if it takes on additional debt to fund the buyback.
The greater the debt load, the more reliant the company becomes on a stable and predictable income, and the more vulnerable it is to the possibility of being unable to meet its debt obligations if sales drop off for any reason.
Another approach is for a company to operate with more debt and less equity, which can make the ROE appear higher.
However, this strategy can also pose risks to the company's financial health, especially if it takes on excessive debt that it cannot service.
It is crucial to note that a higher ROE does not always equate to more money in an investor's pocket since many companies choose to retain their profits to fund future growth.
To gain a better understanding of a company's current operating performance, it is advisable to use the ROE ratio along with other profitability ratios, such as the Return on Capital Employed (ROCE) ratio and the Return on Assets (ROA) ratio.
It is also essential to consider whether a company's lower ROE is due to poor operational performance or is simply a reflection of the industry or market conditions.
For instance, companies in the S&P 500 may have lower ROEs due to their size and maturity.
Ultimately, when computing ROE, it is essential to consider the denominator and the income a company generates from the shareholder's equity.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: What is return on common stockholders equity, and why is it important?
Return on common stockholders equity (ROCE) is a financial ratio that measures how much profit a company generates for every dollar invested by common stockholders. It's important because it gives investors an idea of how well a company is using their money to generate returns.
Q: How is return on common stockholders equity calculated?
ROCE is calculated by dividing a company's net income by its common stockholders' equity. The formula is as follows:
ROCE = Net Income / Common Stockholders' Equity
Q: What is a good return on common stockholders equity?
A good return on common stockholders equity varies by industry and company size, but generally, a ROCE of at least 10% is considered good. However, this can vary based on the company's growth prospects and other factors.
Q: How can a company improve its return on common stockholders equity?
There are several ways a company can improve its ROCE, including increasing sales revenue, reducing expenses, and improving profitability. Additionally, a company can raise more capital from common stockholders or increase its borrowing capacity to invest in new projects or expand existing operations.
Wrap-Up: So, What's Your Next Move?
Return on Common Stockholders Equity (ROE) is a powerful financial metric that can help you take your financial goals to the next level.
However, understanding how it works and its benefits is crucial for you to make informed investment decisions.
ROE is a tool that allows you to measure a company's profitability by examining the returns it generates on the money shareholders have invested.
By analyzing a company's income statement and balance sheet, you can compute ROE by dividing the net income by the equity capital.
A higher ROE indicates that a company is generating more profit with each dollar invested.
In addition to ROE, there are other metrics such as Return on Assets (ROA) and Return on Capital Employed (ROCE) that investors can use to assess a company's performance.
ROA measures the company's ability to generate profits from its assets, while ROCE indicates how efficiently a company is using its capital to generate profits.
It's essential to compare different companies' financial ratios to gain a comprehensive understanding of their performance.
Moreover, dividends to preferred shareholders can also affect a company's performance, and investors should consider this aspect when analyzing financial statements.
However, ROE remains a critical metric for evaluating a company's financial health and performance.
By using ROE as your guide, you can identify businesses that are performing well and make strategic investment decisions that align with your financial goals.
It's worth noting that investing comes with its share of risks, and you should always do your research, seek professional advice, and stay up-to-date with the latest market trends and news.
Keep learning, practicing, and improving your financial knowledge to achieve long-term financial success.
ROE is a powerful tool, but it's not the only metric that you should consider.
By analyzing various financial ratios, you can gain a better understanding of a company's performance and make informed investment decisions.


