Are you looking to up your investing game and make more informed decisions?
If so, you're in luck!
Today, we'll explore a key metric that can help you achieve greater success: the price to sales ratio (P/S ratio).
So, what is the price to sales ratio?
In simple terms, it's a financial metric that measures a company's stock price against its revenue.
It's calculated by dividing the market value of a company's shares by its total number of sales over the trailing twelve months.
The price-to-sales ratio is a powerful tool that can help you determine whether a stock is overvalued or undervalued.
It's also more reliable than the commonly used price to earnings ratio, particularly when evaluating companies in industries where profits are harder to come by, such as biotech firms or tech startups.
One reason the price to sales ratio is so important is that it provides a clearer picture of a company's true value.
While the earnings ratio can be distorted by accounting practices, the price to sales ratio focuses on a company's revenue and is therefore a more accurate measure of profitability.
In fact, numerous studies have shown that companies with low price to sales ratios tend to outperform their peers over the long run.
Successful investors like Warren Buffett and Peter Lynch have used this metric to build their fortunes.
So how can you use the price to sales ratio to your advantage?
By comparing a company's price-to-sales ratio with its industry peers, you can identify undervalued stocks that have the potential to yield significant returns.
This metric can also be used in combination with other financial ratios to paint a more complete picture of a company's financial health.
Understanding the price to sales ratio is essential for making informed investment decisions.
Whether you're a seasoned investor or just getting started, be sure to dive into our in-depth guide on this topic.
By doing so, you'll be well-equipped to take your investing game to the next level and achieve greater success in the stock market.
Definition - What is Price to Sales Ratio?
When comparing companies in similar industries, the price-to-sales ratio (P/S or PSR) becomes an invaluable valuation metric used in ratio analysis to calculate the relative value of these companies.
The ratio formula is straightforward: it involves dividing the stock price of a company by its sales per share.
By doing so, investors can gauge the company's worth with respect to its trailing twelve-month (TTM) sales.
However, it is important to note that the P/S ratio, taken alone, does not provide meaningful data.
It is when we consider this ratio in conjunction with the PSR of several comparable companies that we can truly gain valuable insights.
Comparing the PSR of various companies within the same industry helps highlight potentially undervalued ones.
When assessing the company's market position, the P/S ratio plays a crucial role.
Investors are willing to pay a certain multiple of a company's sales per dollar of stock price.
A low ratio may suggest that investors are undervaluing the company, presenting an opportunity for potential gains.
Conversely, a high P/S ratio may indicate that investors have high expectations for future growth, and they are willing to pay a premium for the company's shares.
It is important to remember that the P/S ratio is just one aspect of a comprehensive financial ratio analysis.
While it helps evaluate a company's valuation, it should be considered alongside other financial ratios to get a holistic view of its financial health.
The P/S ratio can be particularly useful when comparing companies within the same industry, as it takes into account their respective sales and market values.
Additionally, the P/S ratio can also shed light on a company's debt load.
By comparing a company's P/S ratio with its peers, investors can gain insights into how the market perceives its ability to generate sales relative to its total value and debt obligations.
A higher P/S ratio compared to its competitors may suggest that the market views the company as having a stronger ability to generate sales and cover its debt.
The price-to-sales ratio is an important financial ratio that allows investors to evaluate a company's worth relative to its sales.
It is a valuable tool in ratio analysis when comparing companies within the same industry.
However, it should be used in conjunction with other financial ratios to obtain a comprehensive understanding of a company's financial health and market position.
Formula
You can easily calculate the price to sales ratio by using the following formula:
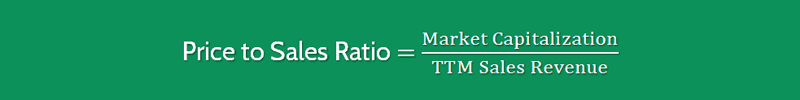
Price to Sales Ratio = Market Capitalization / TTM Sales Revenue
As you can see, to calculate the price to sales revenue ratio, you merely take the market capitalization of the stock and divide it by the TTM Sales.
The number you receive when using this formula is called a sales multiple (or revenue multiple).
A sales multiple of 3 means that the company is worth 3x its sales. In other words, for every $3 of sales, the company is worth $1.
Example
Okay now let’s consider a quick example so you can understand clearly how to calculate the P/S ratio.
Suppose a company has a share price of $10 with 10 million shares outstanding.
Additionally, in the last twelve months, the company has produced $25 million in sales.
To calculate the P/S ratio, the two components of the equation, namely market capitalization and TTM Sales, must be found.
The latter was given, and the former can be computed to be $100 million ($10 per share x 10 million shares outstanding).
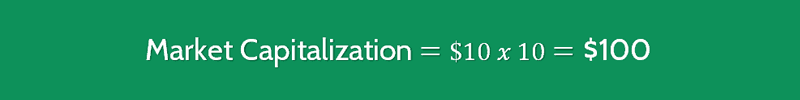
Then, plugging in market capitalization and TTM Sales into our equation, we obtain a P/S ratio of 4.

So in this example, the company in question has a price-to-sales ratio of 4.0.
Interpretation & Analysis
The price to sales ratio, also known as the P/S ratio, is a financial metric that provides insight into a company's valuation.
This ratio is calculated by dividing the company's stock price by the underlying sales over a designated period.
It is often used for comparing companies within the same industry to identify potential undervalued or overvalued stocks.
When analyzing a single company's P/S ratio, it may not reveal valuable data on its own.
However, if we consider the price-to-sales ratios of multiple companies within the same industry, we can gain more meaningful insights.
In such cases, we can potentially spot a company whose revenue is undervalued compared to its peers.
Let's illustrate this with an example.
Suppose we are calculating the P/S ratio for fifteen industrial companies.
Among these companies, fourteen have P/S ratios above 10, indicating that the market values each dollar of their sales at $10 or more.
However, one company stands out with a P/S ratio of 5, suggesting that the market is valuing each dollar of its sales at only $5.
This discrepancy suggests that the company with the lower P/S ratio may very possibly be undervalued.
From a buyer's perspective, it becomes evident that paying $5 for $1 in sales is more favorable than paying $10 or more for it.
This demonstrates the potential advantage of identifying undervalued stocks through the price to sales ratio.
To calculate the price to sales ratio, you can use a price to sales ratio calculator or simply apply the formula to calculate it manually.
The formula involves dividing the company's stock price by its total sales over a designated period.
By comparing this ratio across companies in the same industry, investors and analysts can gain insights into the relative valuation of these companies.
The price to sales ratio is a useful financial metric for assessing the relative valuation of companies.
It allows us to compare how the market values each dollar of sales for different companies within the same industry.
By identifying companies with lower P/S ratios, we can potentially uncover undervalued stocks that may present attractive investment opportunities.
Cautions & Further Explanation
As with any ratio, you must be hesitant to make an investment decision strictly on the results of the price to sales ratio.
While it is possible that a low P/S ratio could be an indicator of an undervalued asset, there exist multiple explanations as to why the P/S ratio would be so low.
For example, a company expecting to generate considerably less revenue in the upcoming year than it did in the previous year, or a company with significantly larger expenses than its peers, would be valued at a lower price than its competitors, thereby yielding a lower sales multiple.
These factors can have an impact on a company's market capitalization, which represents the total value of the company's outstanding shares in the market.
It is crucial to consider the company's market capitalization when analyzing its valuation.
The market capitalization is determined by multiplying the total number of outstanding shares by the current market price per share.
This metric is widely used to determine the overall size and worth of a company in the financial markets.
While the price-to-sales ratio is one of the metrics used to compare companies, it should not be the sole determining factor in assessing a company's financial health.
Growth stocks, for instance, may have higher price-to-sales ratios due to the expectation of substantial revenue growth in the future.
Such stocks may attract much investor attention, leading to higher valuations in the market.
Furthermore, the total sales of the company, which can be found in the financial statements or notes section of the same document, play a significant role in understanding the company's performance.
By examining the company's total sales, investors can gauge its revenue generation capabilities and evaluate its growth prospects.
However, it is important to note that a low price-to-sales ratio does not necessarily imply undervaluation.
Other factors, such as market sentiment, competitive landscape, and future growth potential, must also be considered.
Therefore, it is essential to utilize various financial metrics and ratios, including the price-to-sales ratio, market capitalization, and total sales of the company, to gain a comprehensive understanding of a company's financial health.
Investors should conduct thorough analysis and consider multiple factors before making investment decisions.
By taking a holistic approach to evaluating companies, investors can make more informed choices and mitigate potential risks in their investment portfolios.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: What is the price to sales ratio, and how is it calculated?
The price to sales ratio is a financial metric used to evaluate a company's valuation by comparing its stock price to its revenue per share. It is calculated by dividing the market capitalization of the company by its total revenue over a given period.
Q: How is the price to sales ratio different from the price to earnings ratio?
The price to sales ratio compares a company's stock price to its revenue, while the price to earnings ratio compares its stock price to its earnings per share. The price to sales ratio is often used for companies that are not yet profitable or have fluctuating earnings, while the price to earnings ratio is used for more established and profitable companies.
Q: What is considered a good price to sales ratio?
A good price to sales ratio depends on the industry and the company's growth prospects. Generally, a lower price to sales ratio indicates that a company's stock is undervalued, while a higher ratio may suggest that the stock is overvalued. However, it is important to consider other factors such as profitability, debt levels, and market conditions.
Q: How can investors use the price to sales ratio in their investment decisions?
Investors can use the price to sales ratio to identify undervalued or overvalued stocks and compare companies within the same industry. A low price to sales ratio may indicate a company with growth potential or a potential acquisition target, while a high ratio may suggest that a company's stock is overpriced. However, it is important to consider other factors such as the company's financial health, management, and competitive landscape before making investment decisions.
Conclusion: Unlocking the Power of P/S Ratio
As we wrap up this blog, I want you to take a moment and visualize yourself achieving your financial goals.
Maybe it's a vacation home on the beach, or a comfortable retirement.
Whatever it is, it's within reach.
And the key to unlocking your financial future could be as simple as understanding the price to sales ratio.
The price to sales ratio (P/S ratio) is a powerful tool for investors looking to evaluate stocks.
It provides a valuable insight into the relationship between a company's market price and its sales.
The calculation is straightforward, as you divide the company's market capitalization by its total sales revenue.
By analyzing this ratio, investors can gauge whether a stock is undervalued or overpriced.
A low P/S ratio can indicate an undervalued stock, where investors are paying relatively less per dollar of sales.
It suggests that the market price of the company's shares is not fully reflecting its sales potential.
On the other hand, a high P/S ratio might imply that the stock is overvalued.
In this case, investors are paying a premium valuation per dollar of sales, indicating that the market price might be inflated compared to the company's actual sales performance.
However, the significance of the P/S ratio goes beyond simply identifying undervalued or overpriced stocks.
By understanding and analyzing this ratio, you can make more informed investment decisions and potentially avoid costly mistakes.
The P/S ratio provides a deeper understanding of a company's financial health and growth potential.
For example, if a company has a low P/S ratio compared to its industry peers, it may suggest that the company is undervalued relative to its sales growth and market position.
This could be an opportunity for investors to consider investing in the company before the market recognizes its true value.
Conversely, a high P/S ratio, especially when accompanied by slow sales growth or unprofitable financial performance, may indicate that the stock is overvalued.
Investors should exercise caution and thoroughly evaluate the company's fundamentals before making any investment decisions.
By incorporating the P/S ratio into your investment analysis, you can align your decisions with your long-term goals.
It helps you assess a company's valuation in relation to its sales revenue, providing a clearer picture of its potential for future growth and profitability.
So, whether you're new to investing or a seasoned pro, the P/S ratio is a metric you need to know.
Understanding this ratio empowers you to make more informed investment choices, allowing you to navigate the complex world of stock market investing with confidence.
Keep learning, keep practicing, and keep striving towards your financial success.
With the right tools and mindset, you can achieve anything you set your sights on.


