Are you tired of following the same old investment strategies and not getting the results you desire?
Are you looking for a way to uncover hidden gems in the stock market and maximize your returns?
Look no further than the PEG ratio.
The PEG ratio, which stands for price-to-earnings growth ratio, is a powerful tool that investors can use to evaluate the value of a company's stock relative to its earnings growth.
The PEG ratio formula combines both the price-to-earnings (P/E) ratio and the company's growth rate to give investors a better understanding of a company's true value.
To calculate the PEG ratio, divide the P/E ratio by the expected growth rate of the company.
Investing in the stock market can be a daunting task, but the PEG ratio can help make it easier.
One of the most important aspects of the PEG ratio is that it considers the company's future growth prospects.
By analyzing a company's earnings growth rate, investors can identify undervalued stocks that have the potential for significant growth in the future.
A good PEG ratio is typically considered to be around 1 or lower, indicating that the stock is undervalued relative to its expected growth rate.
Using the PEG ratio, investors can avoid overvalued stocks and focus on companies that have room for growth.
It is a metric that can help investors identify stocks that are trading at a discount to their expected growth rate.
A lower PEG ratio typically indicates that a stock is undervalued, while a higher PEG ratio suggests that a stock may be overvalued.
In summary, the PEG ratio is a powerful tool that can help investors uncover hidden gems in the stock market.
It's a way to find companies that have strong growth prospects and are trading at a discount to their expected growth rate.
By using the PEG ratio, investors can make more informed investment decisions and potentially maximize their returns while reducing their risk.
So why not use the PEG ratio to evaluate potential investments and uncover opportunities for future growth?
Definition - What is PEG Ratio of a Stock?
The price earnings to growth ratio, also known as the PEG ratio, is a valuable tool that takes the price earnings ratio one step further by considering a company's growth prospects.
The ratio is calculated by comparing a company's current share price with its current earnings per share, and then measuring that P/E ratio against the rate at which the firm's earnings are growing.
This offers a more refined look at a potential investment's value, as an attractively high P/E ratio doesn't always hold up under scrutiny once you take the company's growth rate into account.
A rule of thumb for the PEG ratio is that a ratio below 1.0 may indicate that a stock is undervalued, while a ratio above 1.0 may indicate that the stock is overvalued.
However, the interpretation of the ratio can be more complicated than this.
For example, a high growth estimate could justify a higher PEG ratio, while negative earnings could result in a meaningless PEG ratio.
In general, PEG ratios lower than the industry average may suggest that a business is currently undervalued in the marketplace, based on its earnings performance.
On the other hand, a PEG ratio higher than the industry average may indicate that the stock may be overvalued.
It's important to note that the PEG ratio is less useful for companies with unpredictable earnings, since the growth prospects may be uncertain.
To calculate the PEG ratio, you would need to divide the P/E ratio by the expected earnings growth rate.
The growth estimate can be based on either historical or forward-looking data.
However, it's important to keep in mind that the PEG ratio may not always be an accurate indicator of a stock's value, as other factors can also influence its price.
PEG Formula
The formula for calculating this ratio looks like this:
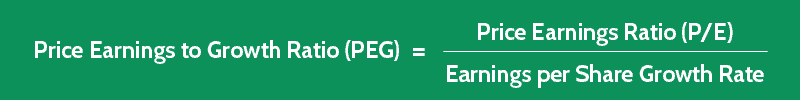
Price Earnings to Growth Ratio = PE Ratio / EPS Growth Rate
Similar to the P/E ratio, with this ratio you have the option of working with either a forward-looking growth rate or a trailing growth rate for this calculation.
Depending on which version of the price earnings to growth ratio formula you use, you’ll end up with different information, all of which can be useful in your investment analysis of a particular business.
A forward annual growth rate generally predicts and examines a period of time up to five years in the future, while a trailing growth rate is based on a company’s established annual earnings growth over the past year, or the average rate from multiple years.
You should bear in mind that when you use a firm’s historical information in the price to earnings to growth ratio, you’ll end up with a factual outcome.
A ratio that incorporates a predicted growth rate for future earnings, while valuable, is still only based on an expectation of a firm’s future financial performance.
PEG Ratio Calculator
Example
Okay now let's consider a quick example to see exactly how to calculate this ratio in real life.
Perhaps you’re considering buying stock in Company KK for your investment portfolio, and you’ve already calculated the firm’s P/E ratio as 10.
Now you’d like to investigate that result further, by taking Company KK’s past and predicted earnings growth rates into account.
By studying Company KK’s financial statements, as well as the analyst predictions for its anticipated earnings growth, you can determine both its trailing and its forward price earnings to growth ratios, as follows:
- Annual EPS Growth Last Year 12%
- Annual Predicted EPS Average for Next Five Years 15%
How do you find the price earnings to growth of this company?
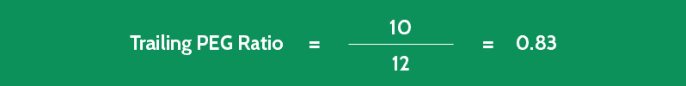
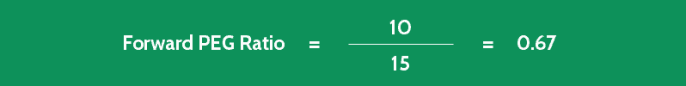
This example shows you that Company KK is currently selling for less than its earnings growth rate. This implies that it’s undervalued in the marketplace.
If the analysts are correct, and Company KK’s earnings continue to grow as predicted, it could represent a good investment for your portfolio.
Interpretation & Analysis
Now that you understand the importance of the PEG ratio, let's dive deeper into how it can help you determine whether a stock is undervalued or overvalued.
The PEG ratio is calculated by dividing a company's price-to-earnings (PE) ratio by its future earnings growth rate.
This ratio is a useful tool for investors because it considers both the current market valuation of a stock and its future earnings growth potential.
A low PEG ratio result is typically an indicator of an undervalued stock.
A ratio of less than 1 is generally considered a good PEG ratio and a good buy.
However, analyzing the PEG ratio is not always a straightforward process.
While a lower ratio may indicate that a stock is undervalued and selling below its intrinsic value, it could also suggest that the stock price is low due to financial difficulties faced by the business.
It's essential to keep in mind that a trailing PEG ratio doesn't offer any insights into a company's long-term prospects.
Also, the analysis of whether a stock is overpriced or underpriced will depend on the type of company and industry it belongs to.
Calculating the PEG ratio allows investors to compare companies with different growth rates and stock prices effectively.
It is a better ratio than the PE ratio alone because it provides more information about the company's future earnings growth potential.
Additionally, the PEG ratio tells you about the company's valuation relative to its earnings growth potential.
It is a valuable tool to use when making investment decisions, but it should always be used in conjunction with other fundamental and technical analysis techniques.
Finally, it's crucial to use the same method of analysis when making comparisons between companies to ensure accurate and consistent results.
How to Use This Ratio to Value Stocks
- Overvalued signal: PEG Ratio > 1.0
- Undervalued signal: PEG Ratio < 1.0
Cautions & Further Explanation
As a wise investor, you should not solely rely on a company's stock price and its peg ratio calculation to determine whether it's a good investment or not.
While the peg ratio is a useful tool to measure a company's growth prospects, it's important to understand that there are limitations to this approach.
For instance, a company's peg ratio may exceed one, which may indicate that the stock is overvalued.
However, if the company is growing rapidly and has a promising future, the peg ratio may not be a reliable indicator of its true value.
On the other hand, a stock with a peg of less than one may appear undervalued, but this may be due to weak growth prospects or declining earnings.
In addition to the peg ratio, there are other valuation ratios, like the PEGY ratio, that can be used to get a more comprehensive understanding of a company's growth prospects.
It's also essential to consider a company's historical and expected growth rates, as well as its industry and market trends.
The Motley Fool recommends that investors should not solely rely on any single ratio or metric when evaluating a company's stock.
Instead, investors should use a combination of metrics to evaluate a stock's potential value.
The peg ratio is just one tool in the investor's toolkit that can be used to evaluate a company's growth prospects, and it should not be relied upon exclusively.
Therefore, it's essential to take into account all available information about a company when making investment decisions.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: What is PEG ratio and how is it calculated?
The PEG ratio (Price/Earnings to Growth) is a valuation metric used to determine a stock's potential for growth by comparing its current stock price to its earnings per share (EPS) and expected future earnings growth. The formula for calculating PEG ratio is P/E ratio divided by the expected EPS growth rate.
Q: How is PEG ratio used to evaluate stocks?
Investors use PEG ratio to assess a company's valuation and growth prospects. A PEG ratio of 1 indicates that a stock is fairly valued, while a ratio below 1 suggests that the stock is undervalued and has the potential for growth. On the other hand, a ratio above 1 indicates that the stock may be overvalued and may not be a good investment.
Q: What are the limitations of using PEG ratio to evaluate stocks?
The PEG ratio is based on future expectations, which can be difficult to predict accurately. Additionally, the PEG ratio does not take into account a company's debt levels, which can have a significant impact on its growth potential. Moreover, PEG ratio should be used in conjunction with other valuation metrics and qualitative factors such as industry trends, management quality, and competitive landscape.
Q: Is a low PEG ratio always better than a high PEG ratio?
Not necessarily. While a low PEG ratio indicates that a stock may be undervalued and have good growth prospects, it is important to consider the reasons why a stock has a low PEG ratio. For instance, if a company has a low PEG ratio due to poor earnings performance or unfavorable industry trends, it may not be a good investment even if the PEG ratio suggests otherwise.
Final Words
Imagine a world where your financial success knows no bounds.
A place where your investments thrive, and your portfolio soars to new heights.
Close your eyes for a moment and envision the possibilities that lie ahead.
Now, open your mind to the power of the PEG ratio – your key to unlocking a future of financial prosperity.
The PEG ratio, short for Price/Earnings to Growth ratio, is the secret weapon every savvy investor needs in their arsenal.
It goes beyond traditional valuation metrics to determine the true value of a company's stock.
Investors value a stock based on the current stock price, but the PEG ratio provides a more comprehensive analysis.
By taking into account not just the earnings of a company, but also its growth potential, the PEG ratio provides an estimate of what investors are willing to pay for each unit of earnings growth.
This information is crucial in deciding if a stock is undervalued or overpriced.
The accuracy of the PEG ratio depends on the quality of the data used to calculate it.
An error in the data can provide an inaccurate PEG ratio, making it difficult to determine the true value of a stock.
The PEG ratio varies depending on the industry, so it's important to compare a company's PEG ratio to others in its sector.
A PEG ratio of 1.0 is considered fair value, while a ratio less than 1.0 may indicate an undervalued stock and a ratio greater than 1.0 may indicate an overpriced stock.
Picture this: you spot an undervalued gem, a hidden treasure amidst the vast sea of opportunities.
Armed with the PEG ratio, you confidently make your move, capitalizing on the untapped potential of the market.
The peg allows you to estimate the potential growth of the company and make informed investment decisions.
But remember, success doesn't come without effort.
Keep learning, stay curious, and practice the art of investment.
The more you delve into the world of finance, the sharper your skills will become.
So, embrace the power of the PEG ratio, and let it guide you towards unparalleled achievement.
Are you ready to embark on this thrilling journey?
The road to financial triumph awaits.
Unleash your potential, embrace the PEG ratio, and let your dreams take flight.
The sky's the limit!


