Are you a value investor looking to analyze stocks and make informed investment decisions?
Then you need to understand the power of the PEGY Ratio.
The PEGY Ratio is a comprehensive calculation that takes into account a company's growth rate, earnings, and dividend yield, all in one easy-to-use ratio.
It's an improvement over other popular ratios such as the price-to-earnings (P/E) ratio since it factors in potential for future earnings growth.
The PEGY Ratio can be particularly valuable for investors looking to identify undervalued stocks with high growth potential.
By focusing on companies with a low PEGY Ratio, you can potentially maximize your returns while minimizing your risks.
This is because a PEGY Ratio below 1.0 indicates that a company may be undervalued.
In addition to identifying undervalued stocks, the PEGY Ratio can also help investors compare companies within the same industry.
By analyzing the PEGY Ratios of different companies, investors can better understand which companies are performing well and which ones may be lagging behind.
This information can be particularly helpful if you're looking to diversify your portfolio or invest in a specific sector.
One of the benefits of the PEGY Ratio is that it includes both earnings growth and dividend yield.
By factoring in dividend payments, investors can get a more accurate picture of a company's financial health.
This is because dividends can be an important source of recurring income for investors.
To calculate the PEGY Ratio, divide a company's price-to-earnings ratio by its projected earnings growth rate and dividend yield.
The result is a comprehensive ratio that takes into account all of the factors that matter most to investors.
In summary, the PEGY Ratio is a powerful tool that investors can use to analyze stocks and make informed investment decisions.
By focusing on companies with a low PEGY Ratio, investors can potentially maximize their returns while minimizing their risks.
By including both earnings growth and dividend yield, the PEGY Ratio provides a more complete picture of a company's financial health than other popular ratios.
If you're looking to take your financial ratio analysis to the next level, understanding the PEGY Ratio is a must.
Definition - What is PEGY Ratio?
The Price to Earnings (P/E) ratio is a widely used financial metric to evaluate a company's earnings.
However, to obtain a more comprehensive picture of a firm's future growth prospects and dividend payouts, the PEGY ratio can be utilized.
The PEGY ratio is an improved version of the PEG ratio as it includes the dividend yield in the calculation.
The PEGY ratio can help investors assess how much they are willing to pay for a company's future earnings growth and dividend payouts.
By dividing the PEG ratio by the sum of the projected earnings growth rate and dividend yield, the dividend-adjusted PEG ratio is obtained.
This ratio can be interpreted as the amount investors are willing to pay for each dollar of the company's earnings, considering its growth prospects and dividend yield.
Incorporating a company's dividend yield in the calculation of the PEGY ratio provides valuable information about the organization's inclination to pay out earnings as dividends.
Therefore, this ratio can be used to measure how attractive a company's future growth prospects and dividend yield are to investors.
Overall, the PEGY ratio can be a useful tool for investors to evaluate a company's earnings, forecast future growth prospects and dividend payouts, and determine its investment potential.
By considering both the company's earnings growth and dividend yield, investors can make more informed investment decisions.
Why Should You Use the PEGY Ratio?
Because this ratio further refines the measure of a firm’s value, beyond either the P/E ratio or the PEG ratio, it’s an even more useful analytical device to include in your investment analysis toolbox.
The Price Earnings to Growth and Dividend Yield ratio offers a number of distinct advantages over the PEG ratio, including:
- Considering both the predicted future growth and the dividend performance of a given company
- Diffusing the possible misconception that a high-growth business is undervalued in the marketplace
- Counteracting the inaccurate conclusion that a high-yield business is overvalued in the marketplace
Considering a company’s dividend performance in your investment analysis calculations is extremely important, since dividends contribute significant value to a business.
Without taking a firm’s dividend yield into account, as the PEGY ratio does, your valuation of a business could be completely off-track.
When an organization has been experiencing high growth, the result of its PEG ratio will be relatively low:
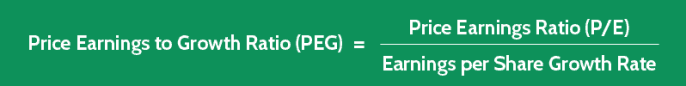
Assume that both businesses have the same Price Earnings ratio (P/E) of 10 (times):
- Company A (normal business) has a growth rate of 10%
- Company B (high growth business) has a growth rate of 20%
Normal Business | High Growth Business | ||
|---|---|---|---|
PEG ratio | 1.0 | versus | 0.5 |
This often leads investors to believe that the high-growth firm is undervalued, and therefore represents a good buy.
- The PEG ratio tends to make high growth companies look to be undervalued, while some of them may be overvalued...
- This causes a potential bias when using this ratio to evaluate your business value
But this is not always the case, since a low stock price will also cause the PEG ratio to be relatively low, and a stock’s price can be low for any number of reasons, including the possibility that it’s in financial trouble:
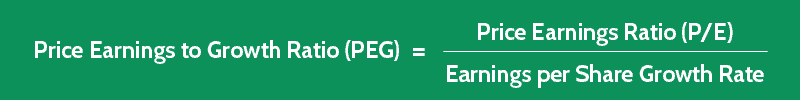
Assume that both businesses have the same growth rate of 10%:
- Company C (normal business) has a P/E ratio of 10
- Company D (low P/E business) has a P/E ratio of 5
Normal Business | Low P/E Business | ||
|---|---|---|---|
PEG ratio | 1.0 | versus | 0.5 |
- The PEG ratio tends to make low price companies look to be undervalued, while some of them may be stuck with financial problems...
- This causes a potential bias when using this ratio to evaluate your business value
Because companies with a high dividend yield also tend to demonstrate a low rate of growth, the PEG ratio result for these firms will be quite high, and they’ll appear to be overvalued in the marketplace.
This can cause potential investors to shy away from what might prove to be a very lucrative stock, and can cause current investors to mistakenly believe it would be a good time to sell their shares:
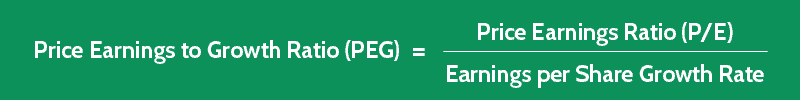
Assume that both businesses have the same P/E ratio of 10:
- Company E (normal business) has a growth rate of 10%
- Company F (high yield business) has a low growth rate of 5%
Normal Business | High Yield Business | ||
|---|---|---|---|
PEG ratio | 1.0 | versus | 2.0 |
- The PEG ratio tends to make high yield companies look to be overvalued, while some of them may be undervalued...
- This causes a potential bias when using this ratio to evaluate your business value
Making use of the Price Earnings to Growth and Dividend Yield ratio, rather than just the PEG ratio, will help you to make better decisions about both your current and your potential investments.
PEGY Formula
To calculate this powerful ratio for a specific company, you would use the following formula:
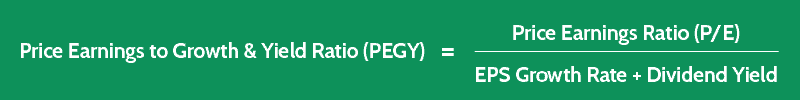
PEGY Ratio = PE Ratio / (EPS Growth Rate + Dividend Yield)
You should note that both the earnings growth rate and the dividend yield are percentage values, but they’re expressed as whole numbers for the purposes of the above formula.
The dividend yield is calculated by dividing a stock’s dividend per share, by its current price.
PEGY Ratio Calculator
Example
You’re in the process of performing a valuation of Company PP’s stock, and have already determined both its P/E ratio, and its PEG ratio.
Now you’d like to calculate Company PP’s Price Earnings to Growth and Dividend Yield ratio, for further analysis.
Your research to date has revealed the following information:
- Current Share Price = $20
- Current Dividend per Share = $2
- Most Recent Earnings per Share = $4
- Predicted Annual Growth Rate = 10%
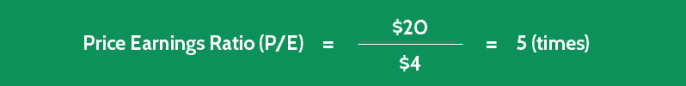
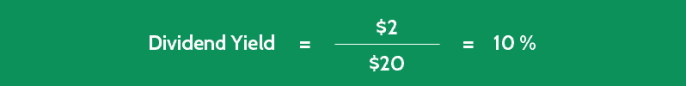
With these figures, you can now calculate Company PP’s PEGY ratio, as follows:

The low ratio of 0.25 indicates that this stock is probably undervalued, and there will be a chance that the stock price will increase in the future.
Interpretation & Analysis
Analyzing the results of the Price Earnings to Growth (PEG) and Dividend Yield ratio for a specific business is a crucial step in determining its equity prospect.
The PEG ratio is a measure of a firm's stock valuation that takes into account its projected earnings growth rate.
On the other hand, the Dividend Yield ratio considers a company's dividend payments.
The PEGY ratio is calculated by combining the two ratios to provide investors with a comprehensive view of a stock's playing field.
So what is a good pegy ratio?
When it comes to determining a good PEGY ratio, a lower result (less than 1) is typically more favorable.
This indicates that the stock is relatively inexpensive in relation to the company's income potential or dividend payments.
Either factor is considered positive since it can indicate that the stock's price is expected to rise.
However, it's important to note that the calculation of earnings growth rate for PEGY is based on a company's expected rate of growth, rather than its actual earnings growth rate.
Moreover, the projection of a stock's future growth prospects is vital to the calculation of the PEGY ratio.
It helps investors understand the stock's high and low points and make informed decisions.
Nevertheless, like most other financial ratios, this ratio result fluctuates from industry to industry.
Therefore, it should always be analyzed against the prevailing norms for a given market sector to make an accurate assessment.
Wall Street analysts typically use the PEGY ratio to assess a company's stock valuation and determine whether a stock is currently selling at a reasonable price.
How to Use This Ratio to Value Stocks
- Overvalued signal: PEGY Ratio > 1.0
- Undervalued signal: PEGY Ratio < 1.0
Cautions & Further Explanation
As an investor, understanding the nuances of a company's financial performance is crucial to making informed decisions.
One of the widely used metrics is the Price to Earnings to Growth Ratio (PEG), as discussed in our previous article.
However, it is essential to note that the PEG ratio is not always indicative of a company's true value.
Without additional information about a company, a high or low PEG ratio can be misleading, making it challenging to determine whether a stock is fairly valued.
Several factors can affect a company's PEG ratio, including its growth rate and dividend yield.
When a firm's growth rate or dividend yield is relatively high or low, it can cause both the PEG and PEGY ratios to be high or low.
For instance, extremely high-yield stocks, such as those that offer a dividend yield of 15% or more, can make it difficult to accurately determine a company's fair value.
The higher yield results in a higher number on the bottom of the PEGY formula, leading to a lower ratio outcome, which may lead you to believe that a stock is undervalued.
However, it doesn't take into account the company's potential for long-term earnings growth or lack thereof, and this can be a significant concern for shareholders.
To account for both earnings growth and dividend payouts, investors often use the dividend-adjusted PEG ratio or PEGY calculator.
It takes into account the sum of the projected earnings and the projected earnings growth rate, as well as the payout ratio.
It's crucial to note that the PEGY calculator's accuracy relies heavily on the consensus estimate used.
A lower consensus estimate can result in a higher PEGY ratio, indicating that a stock is overvalued, while a higher estimate may result in a lower PEGY ratio, suggesting that a stock is undervalued.
The PEGY ratio is a useful tool for evaluating a company's stock performance, but it should not be the sole determining factor when making investment decisions.
It's essential to consider a company's dividend yield and potential for long-term earnings growth to make informed decisions.
You can learn more about other stock valuation ratios here.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: What is the PEGY ratio?
The PEGY ratio is a financial metric that is used to evaluate the valuation of a company's stock. It takes into account the company's price-to-earnings (P/E) ratio, earnings growth rate, and dividend yield. The ratio is calculated by dividing a company's P/E ratio by its projected earnings growth rate, plus its dividend yield.
Q: How is the PEGY ratio used by investors?
The PEGY ratio is used as a tool for investors to determine whether a company's stock is overvalued or undervalued. Generally, a PEGY ratio of less than one is considered to be undervalued, while a ratio of greater than one is considered to be overvalued. However, the interpretation of the ratio depends on the industry and the company's growth prospects.
Q: What are the limitations of the PEGY ratio?
The PEGY ratio is not a perfect metric and has some limitations. For instance, it relies on estimates and projections of future earnings, which can be uncertain and may not materialize. Additionally, the PEGY ratio does not take into account a company's debt levels, cash flows, or other factors that may affect its valuation.
Q: How can I calculate the PEGY ratio for a company?
To calculate the PEGY ratio, you need to first find the company's P/E ratio, which can be obtained from financial websites such as Yahoo Finance or Google Finance. Next, you need to determine the company's projected earnings growth rate, which can be obtained from analyst reports or the company's financial statements. Finally, you need to determine the company's dividend yield, which can also be obtained from financial websites. Once you have these figures, you can plug them into the PEGY ratio formula to calculate the ratio for the company.
Wrap-Up: Sizzle Up Your Investments with the PEGY Ratio
Picture this scenario - you've just invested your hard-earned money in a promising stock, and you're eagerly waiting to see whether it will yield the desired returns or not.
You monitor the stock's performance daily, filled with anticipation, wondering if it will soar or plummet.
If only you had a crystal ball to foresee the future of your investment.
This is where the PEGY ratio comes in - a valuable investment tool that provides an in-depth analysis of a stock's potential by considering its growth rate, earnings, and dividend yield.
By combining the price-to-earnings (P/E) ratio with the company's growth rate and dividend yield, the PEGY ratio presents a holistic view of the stock's financial health.
It is like having a personal financial advisor at your fingertips.
The PEGY ratio's significance goes beyond just the numbers.
It helps investors make informed decisions by identifying undervalued stocks and those that may not be worth the investment.
The metric considers the growth rate and dividend yield of a stock, enabling investors to assess a company's potential for future earnings growth and dividend payments.
Moreover, the PEGY ratio is especially useful for mature companies that pay dividends and use only operating and recurring earnings.
It adjusts the traditional PEG ratio, which only accounts for the growth rate of a company, by including the dividend yield.
If a stock has a high dividend-adjusted PEGY ratio, it may indicate that the stock is overvalued.
On the other hand, a low PEGY ratio may suggest that a stock has a high potential for growth and is currently undervalued.
In summary, if you're looking to enhance your investment game, give the PEGY ratio a try.
This metric is a valuable tool that can help you achieve your investment goals and maximize your returns.
Keep learning and practicing, and who knows, you might become the next investment guru.


